Edge Platforms
Internet of Things
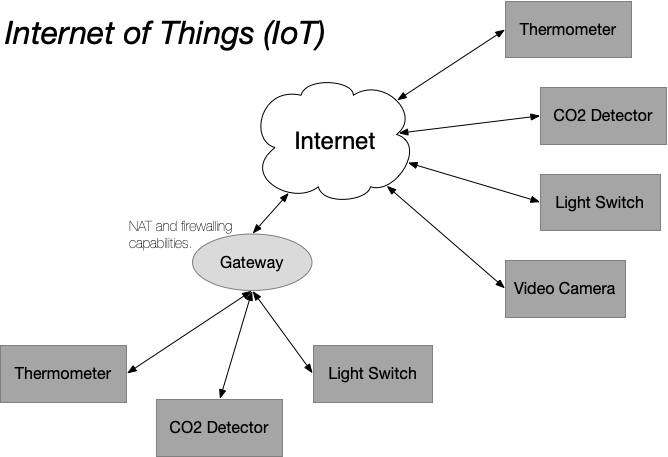
The initial idea for creating a platform of devices (e.g. light controllers, environmental sensors) was simply to have each device connect directly to the Internet. Because the HTTP protocol is so lightweight, embedding this protocol in devices is cheap and easy. This approach is broadly called the “Internet of Things” or IoT.
One technical issue that arises with a pure IoT approach is that the total number of devices in the world easy exceeds the number of available IPv4 addresses. This can be addressed by using NAT with local addresses or by switching to IPv6 addressing. (The IoT issue was one of the motivators for the IPv6 development.)
However, there are deeper concerns with the pure IoT approach. For example, how is security handled and how do you implement proper authentication and authorization for the devices? Unlike the HTTP protocol, adding authentication and authorization, as well as their configuration, is not trivial to accomplish is small, cheap devices.
These concerns are not merely theoretical, there have been a number of distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks that have used IoT devices to amplify the scale of those attacks. The IoT devices used in these attacks often have no security protocols or use default passwords that often not changed.
Edge
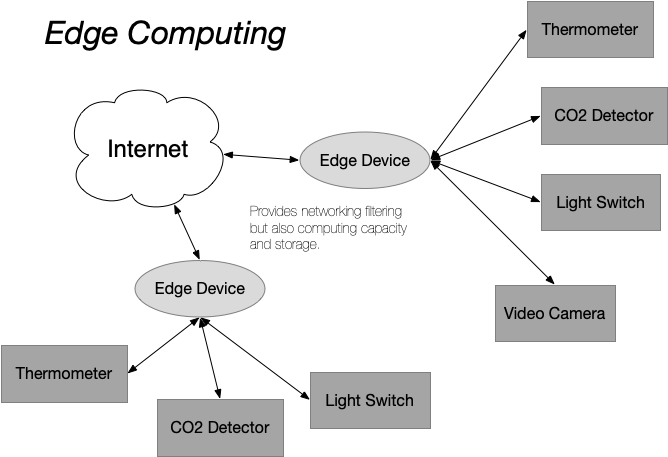
Several trends have contributed to the emergence of edge computing. The security concerns for IoT and limited availability of IPv4 addresses have pushed developers towards the use of gateways. The need for energy-efficient, high-performance CPUs in mobile phones and tablets and make it possible to build gateways that have significant computing capacity, memory, and storage. Lastly, the wide-spread adoption of hybrid cloud computing has provided the framework for structuring IoT devices inside of an edge architecture.
Reflection
Imagine that you want to deploy a smart transport system. What features would you be looking for in an edge platform? Consider all aspects of the platform: development, deployment, operation, maintenance, legal constraints, scale, etc.
What features would you expect when deploying a street lighting system? Again consider all aspects.
What are the similarities and differences between the two cases?